MY SITE
We develop synthetic methodologies for efficient access to complex, bioactive natural products. Here are a few examples:
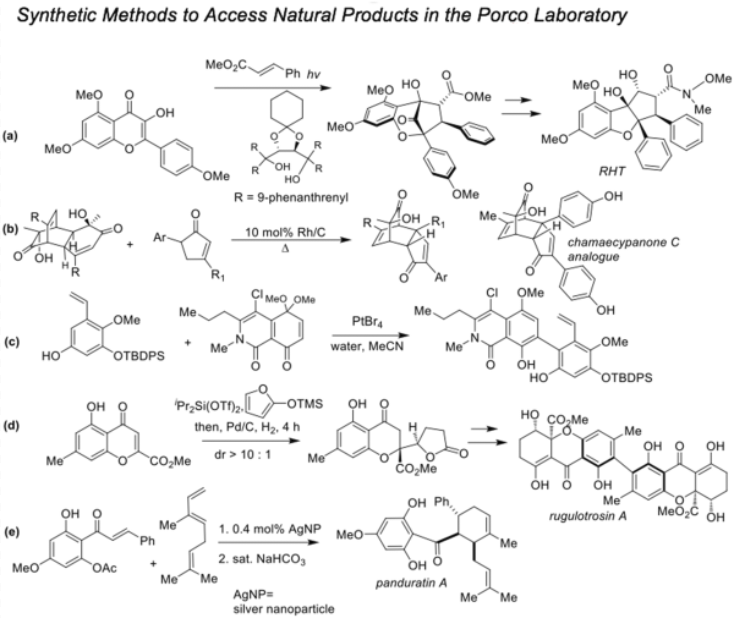
- Our work on excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) photocycloaddition using oxidopyryliums derived from 3-hydroxyflavones (a) enabled rapid syntheses of bioactive rocaglates such as RHT.
- We have published studies on a rhodium-catalyzed dehydrogenation protocol to convert 3,5-diarylcyclopentenones to the corresponding diarylcyclopentadienones and (4+2) cycloaddition with in situ-generated ortho-quinols (b) which led to the synthesis of a highly active analogue of the antitumor agent chamaecypanone C.
- In work towards polycyclic tetrahydroxanthone natural products (PXNP’s), PtBr4 was identified as a novel catalyst for arylation of quinone monoketals with hydroxystyrenes (c) which enabled syntheses of the highly potent anticancer agents kibdelones A and C.
- A concise approach to tetrahydroxanthone natural products employing vinylogous addition of siloxyfurans to benzopyryliums derived from chromones (d) was developed. The methodology led to rapid syntheses of the antitumor agents secalonic acids A and D as well as a seven-step, atropselective total synthesis of the antibiotic rugulotrosin A.
- We have developed silica-supported silver nanoparticles (AgNP’s) (e) as novel catalysts for Diels−Alder cycloadditions of 2′-hydroxychalcones and dienes. AgNP catalysis has been used to synthesize the cytotoxic natural product panduratin A and the acetylcholinesterase (AchE) inhibitor sorbiterrin A in which case AgNP’s were used to mediate a bridged aldol/dehydration event.
Proudly powered by Weebly